Definition of the simple past tense
The simple past tense, sometimes called the preterite, is used to talk about a completed action in a time before now. The simple past is the basic form of past tense in English. The time of the action can be in the recent past or the distant past and action duration is not important.
Examples
- John Cabot sailed to America in 1498.
- My father died last year.
- He lived in Fiji in 1976.
- We crossed the Channel yesterday.
You always use the simple past when you say when something happened, so it is associated with certain past time expressions
- frequency: often, sometimes, always
I sometimes walked home at lunchtime.
I often brought my lunch to school. - a definite point in time: last week, when I was a child, yesterday, six weeks ago
We saw a good film last week.
Yesterday, I arrived in Geneva.
She finished her work atseven o'clock
I went to the theatre last night - an indefinite point in time: the other day, ages ago, a long time ago
People lived in caves a long time ago.
She played the piano when she was a child.
Note: the word ago is a useful way of expressing the distance into the past. It is placed after the period of time: a week ago, three years ago, a minute ago.

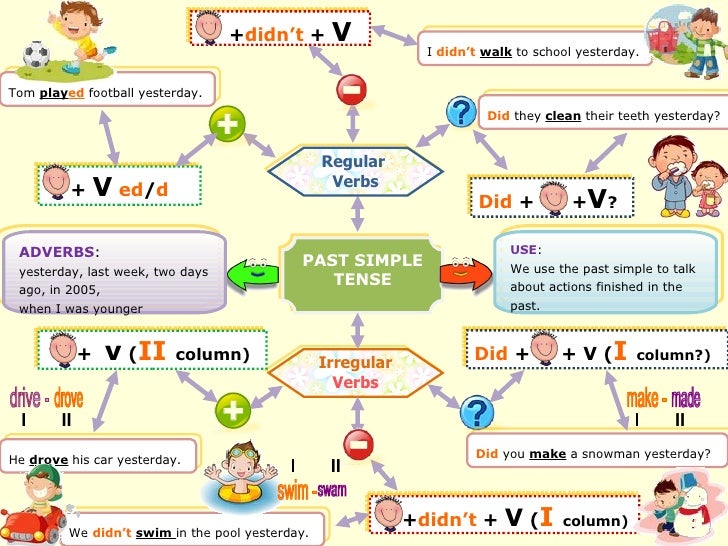
Forming the simple past tense
Patterns of simple past tense for regular verbs
| Affirmative | ||
| Subject | + verb + ed | |
| I | skipped. | |
| Negative | ||
| Subject | + did not | + infinitive without to |
| They | didn't | go. |
| Interrogative | ||
| Did | + subject | + infinitive without to |
| Did | she | arrive? |
| Interrogative negative | ||
| Did not | + subject | + infinitive without to |
| Didn't | you | play? |
To Walk
| Affirmative | Negative | Interrogative |
|---|---|---|
| I walked | I didn't walk | Did I walk? |
| You walked | You didn't walk | Did you walk? |
| He walked | He didn't walk | Did he walk? |
| We walked | We didn't walk | Did we walk? |
| They walked | They didn't walk | Did they walk? |
Simple past tense of to be, to have, to do
| Subject | Verb | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Be | Have | Do | |
| I | was | had | did |
| You | were | had | did |
| He/She/It | was | had | did |
| We | were | had | did |
| You | were | had | did |
| They | were | had | did |
Notes on affirmative, negative, & interrogative forms
Affirmative
The affirmative of the simple past tense is simple.
- I was in Japan last year
- She had a headache yesterday.
- We did our homework last night.
Negative and interrogative
For the negative and interrogative simple past form of "to do" as an ordinary verb, use the auxiliary "did", e.g. We didn't do our homework last night.
The negative of "have" in the simple past is usually formed using the auxiliary "did", but sometimes by simply adding not or the contraction "n't".
The interrogative form of "have" in the simple past normally uses the auxiliary "did".
Examples
- They weren't in Rio last summer.
- We didn't have any money.
- We didn't have time to visit the Eiffel Tower.
- We didn't do our exercises this morning.
- Were they in Iceland last January?
- Did you have a bicycle when you were young?
- Did you do much climbing in Switzerland?
Note: For the negative and interrogative form of all verbs in the simple past, always use the auxiliary 'did''.
Simple past, irregular verbs
Some verbs are irregular in the simple past. Here are the most common ones.
to go
- He went to a club last night.
- Did he go to the cinema last night?
- He didn't go to bed early last night.
to give
- We gave her a doll for her birthday.
- They didn't give John their new address.
- Did Barry give you my passport?
to come
- My parents came to visit me last July.
- We didn't come because it was raining.
- Did he come to your party last week?
CLICK THE LINK : https://prezi.com/view/RuITstOtQ1wRA2ovJFWr/

Comments
Post a Comment